The product manufacturing process can seem long and confusing, and might be enough to stop you from getting started.
In this guide you’ll learn everything you needed to know about the process of creating a new product and bringing it to market. We’ve broken the process down into 5 steps, to help you understand each individual step and what exactly goes into each of them.
- How to come up with an idea for a product
- Ideation Techniques and Methods
- Ideation Tools
- How to have an effective ideation session
2. Research
3. Sampling
- Types of manufacturers
- How to find manufacturers
- Choosing the right manufacturer
- Maintaining a relationship with your supplier

Product ideation
The product manufacturing process begins with an idea for a product. Anything can be a source of inspiration for a new product and when you’re starting out, any idea is a good idea.
During this phrase, you’re not looking for finished or complete ideas yet – you just want an outline or a simple idea that you can expand on and develop more after you’ve completed research.
How to come up with an idea for a product:
Solve a problem: Some of the most popular products have been created because they solve problems that a lot of people have. Think of an idea that you have, or ask your family and friends of any problems that they might have and can be solved by a problem.
Follow a trend: Using social media or the internet you can find out what a really popular trend is and create a product that relates to it.
Improve an already made product: This could be a ‘revamp’ of a product you’ve already created or creating a new product from one you’ve seen from your life. If you’ve found a product you really like maybe you can add new features to it, or there is something you could change to improve it.
Ask your customers: If you’re an already established business, ask your customers what they want to see from you. You can put a survey or questionnaire on your website asking visitors what they want or contact your customers via email.
Ideation Techniques and Methods
Here are some of the most popular ideation techniques and methods that companies and designers use:
SCAMPER
This is one of the most popular ideation tools and helps you create new ideas for products by making you think about how you might improve an existing product. Go down the list and ask these questions about the existing product or idea.
S – Substitute
- What can I substitute to improve this product?
- Can I substitute one part of the product for another one?
- Can I substitute the materials used for the product or the design of it?
- Can I change the name of the product?
C – Combine
- Can I combine this existing product with another product?
- Can I combine ideas, materials, components or features of products?
- What can I combine to lower the cost of production?
A – Adapt
- Is there a part of the product that could be changed?
- Can I adapt ideas from other people’s products?
- Can I adapt or change who your target customers are?
M – Modify
- What can I modify about the product?
- Can I modify the materials, colour, form or shape of the product?
- Can I add extra features to the product?
- Can I add or remove anything from the product?
P – Put to another use
- Are there other ways to use the product?
- Can I change what the product was meant to do?
- Is there a new market or target customers for the product?
E – Eliminate
- What can I remove from the product?
- Is there a way to minimise production or manufacturing costs?
- Is there anything unnecessary about the product?
R – Rearrange
- Is there a way to rearrange or reverse the product?
- Can I rearrange the components, materials or layout of the product?
Using your answers to the questions, do any of them help you to create and develop a new product? This is just the beginning of a new product idea, remember to do more research and planning before deciding on a final product.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is another popular ideation technique that is used to create new ideas. Usually done in a group, people bounce ideas off each other hoping to collaborate and work together to create an idea for a product.
Crazy 8’s
Crazy 8’s is a group-based ideation process and the point is to come up with as many ideas as possible in a short amount of time, focusing on the quantity of ideas and not the quality of them.
- Create 8 boxes on a piece of paper by folding it in half and then half again.
- Set a timer for 8 minutes.
- During the 8 minutes, each person participating in the activity tries to come up with 8 different ideas for a product.
The sketches don’t need to be perfect, they should be rough because the purpose of the task is to create a variety of unique ideas.
When the 8 minutes are up, each participant should present their ideas to the group for feedback.
Mash-Up
This is one of the fastest ideation techniques designed to create ideas out of unexpected things put together. Pick to unrelated categories, like technology or hotels and list as many experiences or products you can from the categories. Combine ideas from the different categories to try and create a new product, experience or service that relates to your business.
The idea of an ideation session is to create as many ideas as possible, they don’t have to be perfect or fully thought out. Try to choose a technique that matches your company, objectives and types of ideas you want to create.
Mindmapping
This visual ideation technique encourages you to create connections between sets of ideas or information. You’ll start by writing a keyword in the middle of a page, related to the problem you’re trying to solve or the idea you have. Then surround the keyword with any ideas that come to mind and try to think of the ways they’re connected – creating a visual mind map.

Ideation Tools
There are a number of online resources available to use to elevate your ideation sessions. Ideation tools are another great way to record and organise ideas and visualise them.
Here are some online tools to help you with the ideation process:
Ayoa
Ayoa is a software tool that brings together mind mapping and task management and collaboration. It works for both teams and individuals and has an all-in-one platform where users can create mind maps, to-do lists, virtual boards for task management and even chat with your other workers with their chat option. There are a variety of different mind mapping options that you can use; each have their own unique styles that can suit your needs.
Brainstorm Cards
Brainstorm Cards is an ideation game, where there are over 50 cards to help you generate new business ideas. This tool is great to help you come up with a large quantity of ideas with very little effort. They’re split into four different trends, regulation trends, market trends, technology trends and customer trends that each cover a separate aspect of society and business.
Creatlr
Creatlr is a platform designed for visual thinking and collaboration that has over 200 templates including mind maps, roadmaps, trend cards, prototype designs, whiteboards and product and market fit canvases.
SessionLab
SessionLab is an online workshop planning platform that offers a large variety of ideation methods with a collaborative approach. There are over 600 facilitation tools and activities that you can include in your workshops and you can easily share your plan with other members in your team.
How to have an effective ideation session
Create a plan beforehand – Make sure everyone involved in the ideation session is clear about what exactly is going to happen. Set a time limit to the session and stick to it. Decide on which ideation technique you want to use, and make sure you have all the materials you need to be able to run it effectively. Have lots of pieces of paper or sticky notes to record ideas!
Aim for as many ideas as possible – The goal of an ideation session is quantity not quality. The more ideas you have, the chances are that one of them will make a great product.
Appoint someone to run the session – You want the session to run as smoothly as possible, so it’s recommended that someone takes charge and runs it. They should decide what ideation session to go with and create a time limit on how long the session will be.
Make it judgement free – Other people in the session shouldn’t criticise or judge an idea. The idea is just to record any ideas that are shared and not become attached to any one idea.
Make sure to follow up – After the session, you should follow up with everyone that participated in it to make sure you don’t lose momentum with creating the product.
Research
Research is a very important part of the product manufacturing process. It’s the step where you’ll decide exactly what product you want to manufacture.
This is where you should ask questions like:
- Who is your target audience?
- What problem is being solved by creating your product?
- Is there a need for your product?
- What is your product trying to achieve?
- What will people get out of the product?
- What problems customers might have with the product?
- Who are your competitors?
- Are there any trends surrounding your product?
- How will you sell your product?
- How will you market your product?
- What will you name your product?

How to validate your idea?
After you’ve come up with an idea for a product and researched the market and your competitors, you need to validate your product idea?
- Researching online demand using Google Trends
- Launch a ‘coming soon’ page on your website to gauge interest with email opt-ins or pre-orders
- Reaching out to potential customers to get their feedback about your product idea
- Interviewing other people in the industry or people who are employed in the industry
- Complete a competitor analysis of your major competitors, their products, sales and marketing strategies
Using Google Trends
Google Trends is an excellent way to see if their is a demand online for the product you want to create. It’s a search feature that allows you to see the popularity of a search term in Google. You can see if a trend is on the raise or decreasing and find insights into certain demographics, regions and related topics and queries. This section will show you how to use Google Trends; for this example, we’re researching the product ‘phone cases’.
Once you’ve entered the product you want to research, you’re able to choose what country you want to search in and a section called interest over time. In this section you can see the search volume for the product over a certain period of time.
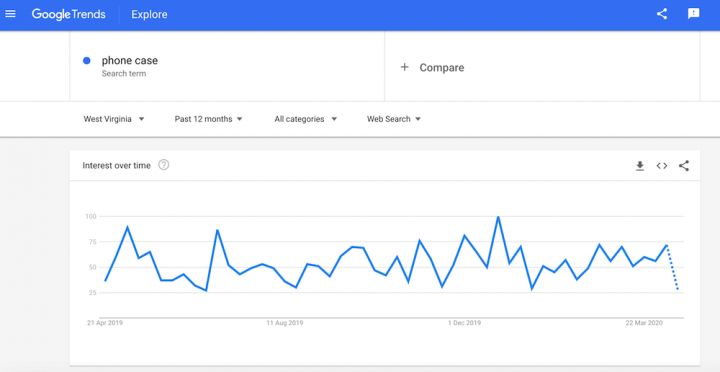
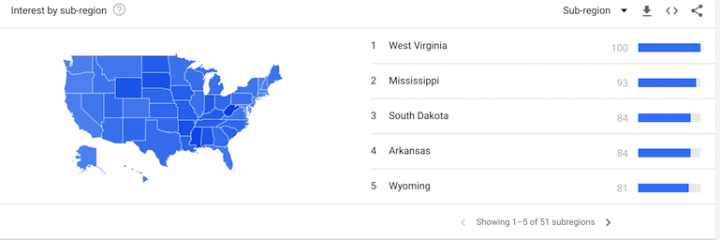
An interesting option in Google Trends is that you can see the search volume in different regions in your selected country. In the phone cases search, you can see that more people in West Virginia than Oklahoma searched for ‘phone cases’. You can even click on the West Virginia section and it shows you the search volume for that sub-region for a certain period of time, and you’re able to do this for every sub-region in your selected country.
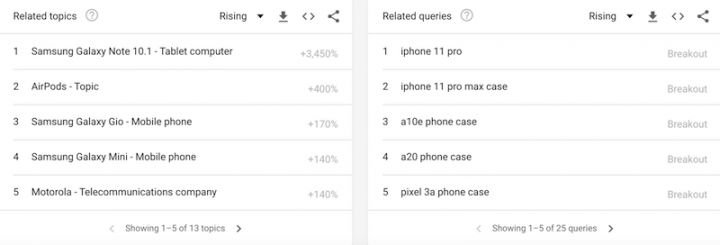
At the bottom of the screen, you’ll be able to see two sections called, related topics and related queries. The lists in both show other terms people who have searched for phone case have also searched for. You can see that there are a number of different types of phones listed – so it might be worth while creating phone cases for those phones.
How to screen your ideas:
If you have multiple ideas for a new product, it’s good to develop a set of criteria to evaluate your ideas against.
The criteria should include:
- Does it fit in with your company’s brand image and values?
- Will your target market actually benefit from the product?
- Does the product fit into the current market?
- Is it feasible to manufacture the product?
- Will the product actually be profitable when manufactured?
- What is the potential appeal to the market?
- Is there enough marketing ideas for the product?
After this, hopefully you should be able to decide on the product you want to create. If you think you have multiple great ideas, save them for later and continue to check the market to see when they could be created and released.
Sampling
The sampling process is one of the most important parts of the product manufacturing experience, because in this step you’ll see your product come to life.
The best way to begin the sampling process is by creating a sketch, drawing or 3D rendering of the final product. It should be as detailed as possible and include a list of the materials you want to use, called a Bill of Materials. When you begin to approach manufacturers and they start sourcing materials, if you don’t know what you need the process will be more difficult. You will also need to think about the colour and design of the product, as well dimensions for the size of the product. Along with the components for the product, you should also start to consider the price you would like to sell it at and where. Will you only sell the product on your website, or will you expand and sell it in stories or at other online retailers?
You should consider all of these questions before contacting manufacturers to create and test your prototype and samples.
Why are product samples important?
Product samples are an incredibly important part of the manufacturing process. There are a number of reasons to have samples when creating a new product, including:
- It makes sure that you’re working with a legitimate manufacturer or factory. It’s a good way to find out whether the factory you’re using has the ability to manufacture the product you want.
- Ensures quality control. In order to create products your customers will actually buy, they need to make sure they’re high quality. You don’t want your customers to get a product that doesn’t work the way it’s supposed to, or doesn’t fit. Requesting samples from a manufacturer allows you to see the quality that your product is going to be.
What is the sampling process?
These are some of the samples you can request from your manufacturer or supplier. These examples relate to the apparel industry, but are commonly used samples in all industries.
1. Mock-up sample
A mock-up sample is the first sample you will request and it is just a very basic interpretation of your idea and product. This sample doesn’t include any of the finer details of the product and may not even be in the same fabric as your final product. The mock-up sample is simply there to help visualise the specifications of your product. There might be multiple mock-up samples from your manufacturer before you finalise it and move on to the next step.
2. Garment performance test (GPT) sample
These samples are used in tests in order to see how your garment will perform. The tests can include seam and tear strength, colour fastness to rubbing, perspiration and water, shrinkage and wash fastness. The tests should be done by your manufacturer in their factory and they send the results to you.
3. Pre-production sample
A pre-production sample is made with the fabric, trims and accessories that your final garment will be made with. It should be made with your exact specifications, measurements and any other details you want the final product to have. These samples give your company and your manufacturer the opportunity to be in agreement about the garment and its construction, fit and design. Usually once this sample is approved, your product can be mass produced.
4. Top of production (TOP) samples
Top of production samples are the first items in the production line that are checked for their quality. This is done to make sure the mass production is of the same quality and standard as the pre-production sample. It also helps to ensure that the products in the production line are set up in line with your original vision for the product and meet the specifications you wanted.
5. Shipping samples
Shipping samples show what the customer buying the product will be sent when the product is shipped to them. It will show the packaging, bagging or wrapping of the garment and the labelling. Once this sample has been approved, you can start selling and shipping your garment.
How to ask for samples from your manufacturers?
Once you have found a supplier that you would like to work with, the next step is to contact them and request a sample from them. The easiest way to contact them is via email, especially if you’re using an international supplier. If you can, you can also contact them by calling them, or if they have a store, visiting them in person.
You should ask them:
- About the company’s background and their reputation
- Whether they can manufacturer the product you want to sell
- What is their MOQ
- What will the cost be
- What shipping options they have
- What is their quality control process
- How do they handle their customer service
If you want to know more about the sampling process, read our article A Guide to product samples: how many rounds do you need and how do you get them made?
Manufacturing
When you start looking for someone to manufacture your products, you will come across a variety of different suppliers.
Here are some of the different types of suppliers:
Manufacturers: A manufacturer is a company that has a factory that makes your product and sells it directly to you or a wholesaler. Manufacturers are known for requesting high MOQ’s, meaning that you will have to order your products in bulk. Using a manufacturer is a big financial investment upfront, but you’ll be making more profit with each sale and getting your products for a very low price.
Wholesalers: Wholesalers purchase products from manufacturers and resell them to other businesses for a higher price. They have the ability to purchase bulk items for the lowest price, and the more stock you buy from them, the lower the per-item cost will be. The products you buy from them are shipped to your store, and you send them to the customer.
Dropshippers: Dropshipping companies are very different from wholesalers and manufacturers because they deliver the products you buy directly to your customer’s door. Dropshipping is a cost effective way to manufacture your products, because there is no need to store them anywhere or ship them from your store. You only have to pay the dropshipping company the wholesale price for the product and a small shipping fee.
Trading companies: Trading companies do not manufacture products, they are middlemen that source products from manufacturers and then increase the price of the products and resell them. Trading companies are often used when companies are wanting to use an international supplier because they usually provide translators to help with communication.
Sourcing companies/agents: Sourcing companies are also a third-party that helps companies find suppliers or manufacturers to create their products. They can be expensive to work with, especially if you only plan on ordering a small quantity of products. You also have to know exactly what products you’re after, because sourcing companies help to find specific products.

How to find manufacturers
For new companies, finding manufacturers that offer high quality products, fit their brand and offer a reasonable price can be hard. Before you start looking for manufacturers, make sure you know exactly what product you want made, the materials needed to make the product and the price you want to sell it at. Once you know these, there are a number of ways to find manufacturers including:
The internet – A very simple way to find suppliers and manufacturers is through a quick Google search. You are able to find suppliers near you, in your industry, their contact information – so you can contact them quickly and easily – and reviews from other companies that have used them.
Trade shows – One of the best places to find suppliers is at a trade show, where you’ll be able to speak to people from the company face-to-face to ask questions, get information from them directly and compare other suppliers in person.
Trade publications or magazines – There are a number of magazines and publications that feature manufacturers specific to your industry or market.
Online forums – Online forums are another great way to find suppliers or manufacturers. They have information from real people that have used these companies and can review and give you feedback about the supplier you’re looking at using. You can also use online forums to contact suppliers or manufacturers directly.
Facebook groups – Depending on your industry or market, chances are you’ll be able to join a Facebook group that has people in it that can share their experiences about manufacturers. They can give you information and feedback about their experiences and positive and negative insights on specific suppliers.
Choosing the right manufacturer for your business
Actually choosing the right manufacturer or supplier is a crucial part of the product manufacturing process. Before you decide to begin working with a manufacturer, ask them a series of questions to make sure they fit your brand.
What is your lead time?
You want to work with a manufacturer that works with your time frame, but remember to keep in mind it might differ depending on your product and how many you want made.
What are their payment terms?
When it comes to paying a down payment, you should expect to pay less than or 50% of the total cost. If they ask for more than that, or the full amount it’s a big red flag and you should find another supplier.
What is their quality assurance process like?
The manufacturer you want to work with should be able to provide you details of their quality control process. You need to make sure that they have the necessary steps in place to make sure that your products are of the highest quality.
Where do they get their materials from?
Asking where your manufacturer gets their materials from can help to ensure that they are of the highest quality. They should be able to provide all of the details of what materials they use and where they get them from.
Maintaining a relationship with your manufacturer
Creating and maintaining a relationship with your manufacturer or supplier is an incredibly important part of the product manufacturing process and can determine whether your company is a success or not. Once you have found a good supplier that works for your company, you’ll want to work with them for as long as possible, so having a good relationship is important.
You can do this by:
Focusing on effective communication: Communication is essential to maintaining a good relationship with your manufacturer. You need to stay in regular contact with them and keep them up to date on how much stock you have, and how long until you need to order more products. Communication is also really important if you have an issue with your manufacturer. You should let them know as soon as possible if you have a problem, so it can be solved without too much of an issue.
Be honest and upfront: Be honest with your manufacturers about your needs and expectations, you can’t expect them to know everything you want or be able to predict it. Don’t constantly change your mind and expectations with things like lead time or design, because you will use the trust of your manufacturers and they won’t be happy.
Pay on time: You should aim to consistently pay your bills fully and on time. If you can’t, you should aim to let your manufacturer know in advance. Creating a contract that specifies payment terms that you both can follow is the easiest way to make sure there are no problems.
Companies will even use a Supplier Relationship Management Solution to ensure all their communications are in the same place.
Product Launch
Now that you have decided on the final product and it’s being manufactured, you need to launch it.
You need to decide on a launch date, if you haven’t already throughout the process, how you will launch the product and how you’ll market the product. The marketing campaign can include email campaigns, billboards or posters, paid media advertising, social media marketing and advertising on websites.
Through customer feedback and reviews, the product manufacturing process is never really over. You can use the feedback to constantly improve or update the product.

The complete product manufacturing process can be stressful and take quite a long time. We hope this article has helped you understand some of the most important aspects of the process and helps you get started with creating your own product!



